As desirable targets for cybercriminals, insurance companies must comply with strict data protection requirements. Non-compliance often leads to data breaches and considerable fines.
In this article, you’ll learn about eight data protection best practices for insurance organizations to comply with relevant laws, regulations, and standards and safeguard your customers’ sensitive data.
Types of data insurance companies work with
If banks hold the money, insurers hold the data.
Insurance organizations process their customers’ personal data to underwrite risks and provide the most favorable services. Personal data is the lifeblood of insurance services, as only comprehensive and accurate information about customers allows insurance companies to provide viable and sustainable offerings.
For instance, insurance providers need data about customers’ health and criminal convictions to achieve risk-based premium pricing and process claims. In the case of employee-sponsored insurance, the insurance company needs an employment contract as the legal basis for creating a policy.
Depending on the type of insurance services provided, insurers collect a wealth of data on individuals covering their health, property, vehicles, and even pets. Here are the most common types of sensitive data in the insurance industry:
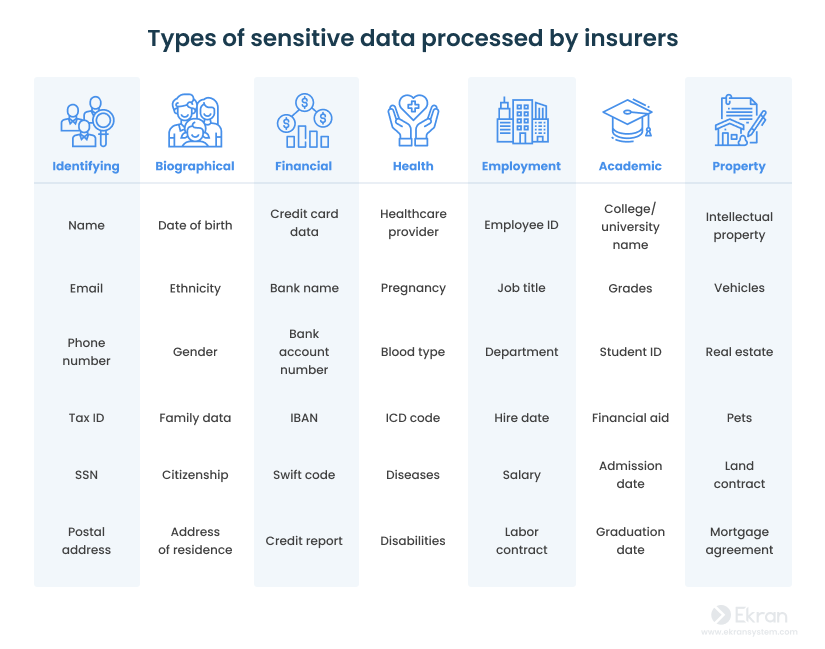

As you can see, most of the data collected by insurance organizations is personal and vulnerable and, therefore, must be well-protected. In the next section, we provide insights on recent data breaches in the insurance industry.
7 Best Practices for Banking and Financial Cybersecurity Compliance
Data breaches in the insurance industry
Where does the threat come from?
Cyber attacks in the insurance industry often don’t exploit system vulnerabilities but instead target careless employees and subcontractors.
According to Verizon’s 2022 Data Breach Investigations Report, the most common outsider attacks on companies in the insurance and financial industries are phishing, credential theft, and ransomware attacks. Employees often make errors, such as misdelivering valuable data. There are also malicious insiders who may conduct insurance fraud, aiming to benefit financially from defrauding their employer.
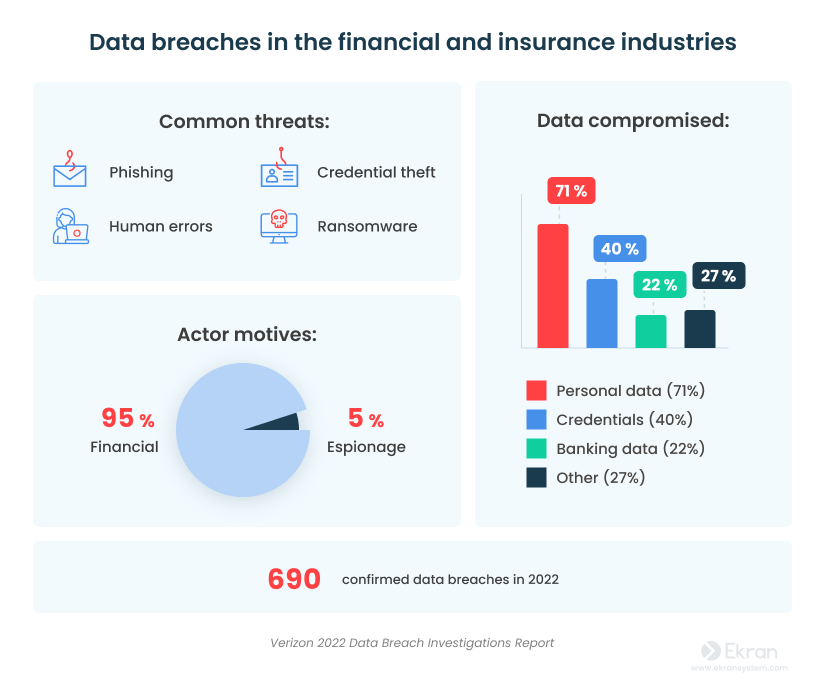

Here are several recent high-profile data breaches of insurance organizations:
- The Australian health insurance company Medibank suffered a massive data breach in October 2022. The incident started when credentials were stolen of a user with privileged access to Medibank infrastructure. Those credentials were sold on the dark web and then used to access Medibank clients’ sensitive data. As a result, perpetrators managed to extract 200 GB of data that included personal details of 9.7 million Medibank customers.
- In January 2023, a vendor’s vulnerability caused a data breach in Aflac Inc., headquartered in the United States. Hackers compromised 1.3 million records of Japanese cancer insurance policy holders. Compromised information included policy holders’ names, age, gender, and type of insurance.
- Nearly at the same time as the Aflac incident, a data breach involving a third-party contractor happened in Zurich Insurance Group. The incident resulted in the disclosure of data of over 757,000 current and former automobile insurance policy holders. Disclosed information could have included last names, gender, dates of birth, email addresses, vehicle brands and models, etc.
Data breaches may result in loss of customer loyalty and considerable fines. They may even jeopardize insurance businesses. This is why protecting personal data should be the main priority for the insurance industry.
Insider Threat Statistics for 2022: Facts and Figures
Compliance requirements for the insurance companies
Reduce the risk of data breaches with regulatory compliance.
Insurance providers are obliged to follow data protection requirements and can face strict penalties for non-compliance. Let’s take a look at the major regulations, acts, and standards that require data protection in the insurance sector.
Depending on the type of sensitive data collected and processed in order to provide insurance services, organizations have to comply with the following:
To protect personal data:
- The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) aims to secure personal information of European Union residents. Insurers that provide services to EU residents must comply with GDPR requirements regardless of where their business is registered and where business activity occurs.
- The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) controls the collection, use, and sale of personal information of California residents. Insurance companies operating in California are subject to the CCPA, which includes disclosure obligations and requirements related to consumer privacy rights.
- The Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) regulates how private sector organizations collect and use personal information of Canadian residents for commercial activity. Insurers across Canada are obliged to comply with PIPEDA requirements.
To protect healthcare data:
- The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) places rules on how health-related data can be collected, stored, and processed in the US. HIPAA aims to prevent fraud and abuse of personal healthcare data. US insurance providers dealing with medical records are required to implement adequate healthcare data protection to avoid fines for HIPAA violations.
To protect financial data:
- The Gramm–Leach–Bliley Act (GLBA) is a US law that requires insurance companies to explain their information sharing practices to customers and to protect customers’ sensitive data. It also obliges insurers to track employees’ activities, especially those that relate to accessing customers’ protected records.
- The Sarbanes–Oxley Act (SOX) aims to make the activity of US insurance organizations more transparent and secure. It also prevents fraudulent actions and protects financial records. To meet SOX requirements, insurance organizations use dedicated SOX audit software and have to document every communication and financial operation.
- The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) safeguards the security of credit card processing. Insurance providers around the world must have a PCI DSS compliance system if they accept credit cards or store information about them (such as for payment of insurance policy premiums).
Note: In addition to these major data protection measures, insurance organizations may also have to comply with other local and international laws and regulations regarding customers’ personal data.
How to Pass an IT Compliance Audit
8 best practices for data protection compliance in the insurance industry
Take these steps to ensure compliance with data protection requirements.
Complying with data protection requirements can be a real challenge for insurance companies. Here’s a list of eight best practices that will help you properly protect your customers’ sensitive data with minimal effort:


1. Appoint a data protection officer
Designate one or more employees to control data protection measures in your organization. Meeting this GDPR and PCI DSS obligation will greatly assist you with ensuring data protection, passing security audits, and responding to security incidents.
2. Conduct a risk assessment
Before protecting your customers’ information, you need to know what types of sensitive data you work with and how this data is stored and processed. Only after identifying your valuable assets can you assess the cybersecurity risks and start mitigating weak spots in your data protection.
3. Ensure secure access to data
Protect access to your critical assets by implementing the principles of zero trust or least privilege. These principles allow you to control who can access your customers’ information and what actions they can perform with data. You can protect access to your IT infrastructure with multi-factor authentication (MFA). As well, consider using password management solutions to safeguard the use of passwords within the organization.
4. Monitor user activity
Employee activity monitoring is one of the main requirements of cybersecurity acts, standards, and regulations including SOX, PCI DSS, and GLBA. Some dedicated IT security solutions allow you to continuously record all employees’ actions with sensitive data without jeopardizing employees’ privacy. Modern solutions with AI-based behavior analytics [PDF] can immediately inform you about any abnormal employee activity and help you prevent a data breach long before it happens.
5. Manage privileged users
Employees with privileged access to your IT infrastructure are the most common targets of cyber attackers. To prevent unauthorized access, consider using privileged access management (PAM) solutions that can help you control user privileges and monitor activity of privileged users. To avoid credential abuse, you can enhance privileged user access with one-time passwords or time-based access restrictions.
Privileged Access Management: Essential and Advanced Practices
6. Reduce third-party risks
Most data protection regimes require you to monitor who accesses important data and for what purposes. You may be required to audit insurance applications that third-party service providers are using for accessing customer data or check server access directly. Therefore, the best way to ensure security compliance and data protection in the insurance industry is to monitor third-party vendors using dedicated cybersecurity tools.
7. Encrypt data
To ensure the safety of critical data both at rest and in transit, make it unreadable for those who might obtain it. Data encryption is required or recommended by the GDPR, LGBA, PCI DSS, and other regulations, laws, and standards. Use encryption to avoid the compromise of customer information in case of a data breach. This measure can also save you from paying millions of dollars to affected customers.
8. Prepare for a fast incident response
An incident response plan will help you mitigate the consequences of a data breach and is part of most compliance requirements. You can make an incident response plan as a separate document or as part of your cybersecurity policy. With this plan, cybersecurity officers and regular employees will know what actions they should take for each type of security incident, who they should inform, and within what time frames. The time frames for notifying a supervisory authority about a breach of personal data vary. For instance, the GDPR sets a 72-hour notification deadline after you become aware of a cybersecurity incident.
All these best practices to comply with data protection requirements will improve the security of your insurance organization, help you avoid penalties, and increase customer trust and loyalty. To easily implement them, consider deploying dedicated HIPAA, SOX, PCI DSS, or GDPR compliance platforms.


Meet data protection requirements with Ekran System
Comply with many requirements using one solution.
Deploying designated cybersecurity software for employee monitoring will allow you to process and store customer data securely and in compliance with relevant laws, regulations, and standards. With Ekran System deployed as an insider risk management platform, you’ll get more than just user activity monitoring.
Ekran System offers the following functionality for insurance company cybersecurity compliance:
- User activity monitoring (UAM) for controlling employee activity in real time and recording user sessions in video format with helpful metadata on user activity
- Monitored data anonymization for removing personally identifiable information about your employees and partners and protecting their identities from accidental disclosure
- Privileged access management (PAM) for granularly controlling access to critical endpoints and getting full visibility over the activity of privileged users
- Identity management for ensuring that only authorized employees have access to your critical assets (two-factor authentication and additional credentials for shared accounts can be used to verify user identities)
- Real-time incident response for getting notified of suspicious events so you can respond to them quickly by warning and blocking users
- Enhanced auditing and reporting for generating advanced reports in a searchable format and investigating security events in detail using session analysis capabilities
As an all-in-one cybersecurity solution, Ekran System can enhance your corporate security to meet multiple data protection requirements in one go.
Meeting IT Compliance Requirements
Conclusion
Meeting numerous data protection requirements may be challenging for insurance providers. Make sure to leverage the best practices from this article and use a robust security solution to reduce compliance overhead.
All-in-one solutions like Ekran System can simplify compliance with data protection requirements and industry standards by providing your organization with user activity monitoring, privileged access management, incident response, and other data protection functionalities.
Request a free trial of Ekran System to protect your sensitive data!





