Knowledge is power. Especially in the hands of your competitors.
Information about your company, its products and services, finances, sales, and marketing strategy is a weapon of modern economic warfare.
That’s why it’s important to ensure that your organization’s data is well-protected.
In this article, we explain (with real-life examples) how corporate spies attack and discuss how to prevent industrial espionage. You will learn what measures to take to keep your business secrets safe and sound.
What is industrial espionage?
Intelligence on competitors gathered in a legal way can give you a leg up in the fight for market share.
But sometimes, companies and governments want more.
Competitors and governments send agents to spy on critical information more often than you might think. According to NBC News, “The FBI opens a new China-related counterintelligence investigation every 12 hours on average.”
The financial consequences of industrial espionage are significant:
According to Mike Orlando, the director of the National Counterintelligence and Security Center, the annual cost of solely Chinese espionage in the United States is estimated at approximately $600 billion.
Unlike competitive intelligence, industrial espionage means embracing illegal and unethical methods of collecting corporate data to gain a competitive advantage. It involves compromise of trade secrets and intellectual property theft.
There is some ambiguity around types of industrial espionage. R. E. Wagner distinguishes two: industrial espionage itself (which can also be referred to as corporate and commercial espionage) and economic espionage. The main difference lies in who’s the coordinator.
While industrial espionage is controlled by and benefits private companies, economic espionage is governed by foreign states.
Here’s where things get tricky:
The interests of governments and companies frequently overlap, making it hard to distinguish between these two types of espionage. Consequently, we will be using ‘industrial espionage’ as a generic term in this article unless we want to stress the specifics of economic espionage.
Now, let’s see who’s most at risk of becoming a target for industrial spies.
Targets of industrial espionage
Is your company at risk?
Industries that heavily rely on research and development (R&D) – including the computer hardware manufacturing, IT, automotive, energy, aerospace, and chemical sectors – should be extra cautious. R&D often involves innovative solutions and technologies that are costly to develop, making them a desirable target for spies.
Industrial espionage is also common among the retail, financial, and public sectors, as they have high competition and often suffer from a lack of investment in cybersecurity.



Pay special attention to protecting the following data in your organization:



- Trade secrets. A trade secret generally means sensitive information about existing products or products under development. This information may help your rivals get a competitive advantage.
- Client information. Data about your clients, including their financial information, can be exploited to steal your business. Another possible scenario is leaking illegally acquired data to damage your company’s reputation.
- Financial information about your company can be used to offer better deals to your clients and partners, win bids, and even make better offers to your valuable employees.
- Marketing information. With this information, competitors can prepare a timely answer for your marketing campaigns and make them ineffective.
5 Industries Most at Risk of Data Breaches
Methods of industrial espionage
How does industrial espionage affect your business? Spies can breach your security and illegally obtain data in the following ways:
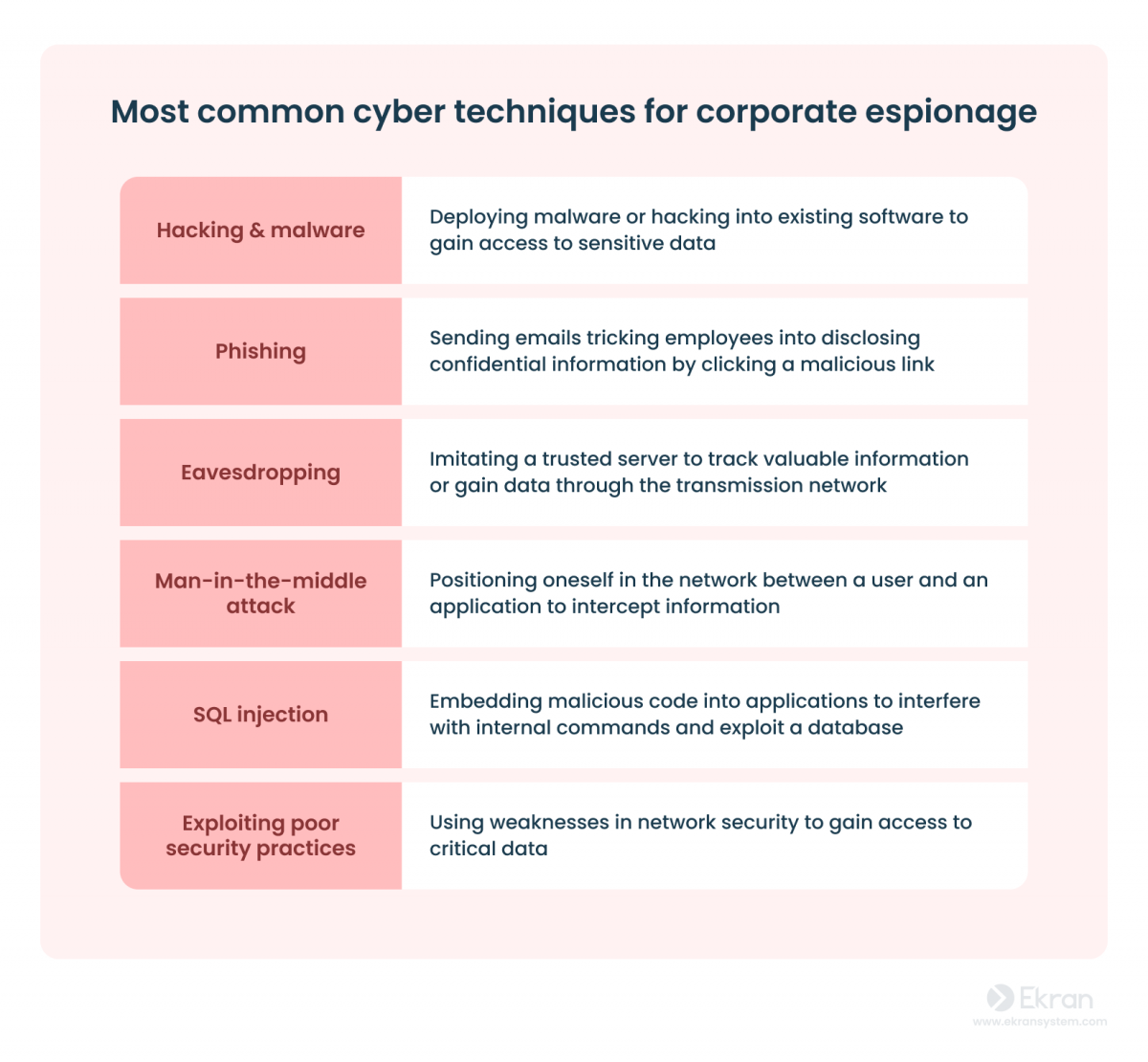
Cyber attacks
Cyber attacks are hostile attempts to steal, compromise, change, or destroy information by gaining unauthorized access to an organization’s computer systems.
Hackers or outsider attackers are frequently involved in industrial espionage. They can gain access to your sensitive data by exploiting known and zero-day vulnerabilities.


How to detect cyber espionage?
The risk of a cyber attack is a well-known nightmare for organizations. However, knowing the risk doesn’t always make companies take necessary measures. Many companies still don’t have a cyber espionage prevention strategy in place.
The majority of companies have up-to-date malware protection and network security, but only a few think about incident response plans, control of storage devices, and formal policies.
Moreover, cyber breaches are often preceded by physical access that makes them possible. That’s why even sophisticated anti-malware protection and firewalls are not enough when insider and cyber threats are linked.
12 Cybersecurity Best Practices to Prevent Cyber Attacks in 2023
Insider threats
In acts of industrial espionage between companies and states, malicious insiders are used more frequently. Competitors can send their spies to your company to act as your regular employees while secretly gathering intelligence for their actual employer.
Competitors can also approach your trusted employees who have privileged access, asking them to trade your corporate secrets and other valuable information and offering them money or blackmailing them into cooperation.
In both cases, the illegal actions of such employees are much harder to detect than hacking attacks, making insider activity a safer bet for malicious actors.
If you think your employees are not like that…
Workers can also perform or aid in corporate espionage inadvertently. Various social engineering techniques can be used to gather secret information or extract credentials from employees.
As an illustration:
A USB stick left in a hallway for a curious employee to pick up and insert into a corporate computer can initiate a massive data breach and cost your company a lot of money.
Former employees are another source of danger. A disgruntled employee looking for a way to get back at the company – or simply a trusted insider leaving for a competitor – could easily take an organization’s sensitive data with them.
Portrait of Malicious Insiders: Types, Characteristics, and Indicators
But it gets worse:
Corporate espionage has become even easier to perform after the outbreak of the coronavirus pandemic, when companies had to switch to remote work. While telecommuting gives employees flexibility, it also introduces new cybersecurity risks.


Why is industrial espionage often unnoticed?
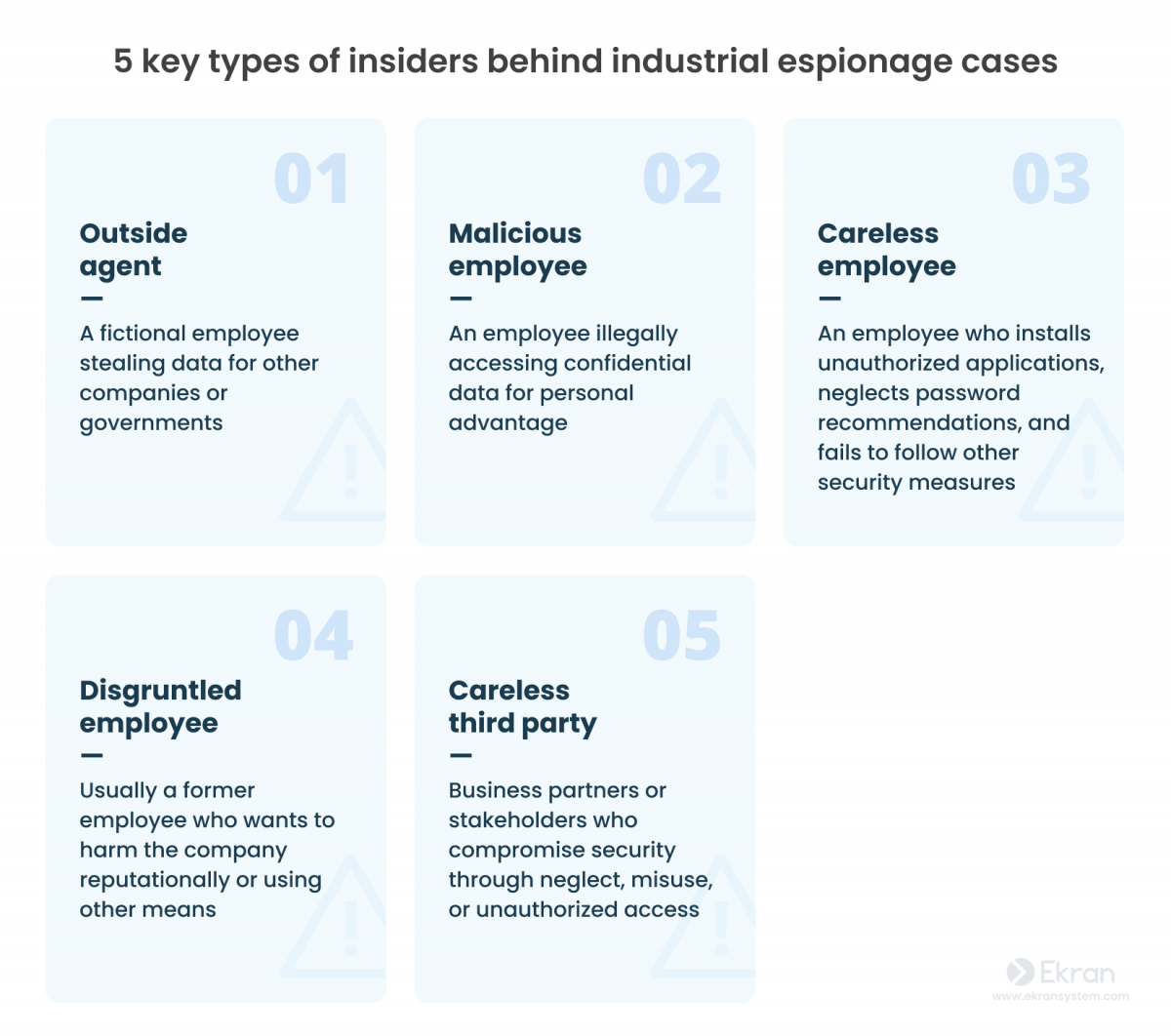
Industrial espionage is hard to detect and even harder to prove.
You might have heard of sensational espionage cases in the news. The truth is:
They’re just the tip of the iceberg.
Industrial espionage is an illegal yet widespread practice. If it hasn’t affected your company, it’s only a matter of time.
There are several reasons why most companies do not report cases of industrial espionage:
- Industrial espionage is hard to identify. Most malicious actions of insiders remain indistinguishable from normal everyday activities. Even your most valuable employee with access to sensitive data may act as a double-agent without your notice for a long time.
- It’s hard to hold perpetrators accountable. Laws on trade secrets and industrial espionage vary across the globe. If you have detected an international spy, it may be very hard to hold foreign companies and governments accountable. And even if the perpetrator is domestic, they can prolong legal procedures to the point where it’s not feasible for your company to continue pursuing the case.
- It may harm your stock price. The value of your company’s stock may fall if it becomes publicly known that your security has been breached. Such knowledge may undermine the trust of your investors and customers as well.
- It can be seen as a violation of IT compliance requirements. A company is responsible for ensuring the security of its customers’ sensitive data. In certain countries and industries, if this data is leaked or stolen by industrial spies, the company will be fined. Yes, you may be penalized even in the event of suffering from industrial espionage.
All of these factors compel companies to keep cases of espionage to themselves and conduct internal investigations. It’s an organization’s responsibility to establish effective detection and response procedures. Building an insider threat program and taking effective prevention measures are the best way to deal with industrial espionage.
7 high-profile industrial espionage cases
Even the tech giants can fall victim to industrial spies.
Although most companies try to hide instances of industrial spying to protect their reputation, there are cases that have become known to the public.
Let’s take a look at publicly known industrial espionage examples:
Coca-Cola
In April 2021, a former Coca-Cola employee, Dr. Xiaorong You, was convicted of stealing trade secrets related to bisphenol A (BPA). She was accused of conspiracy, wire fraud, and economic espionage. To bypass Coca-Cola’s security measures, Dr. You took photographs of secret documents with her phone.
As the story in Chemical & Engineering News reveals, the Chinese chemist stole information from Coca-Cola and seven other chemical companies worth a staggering $120 million. Dr. You planned to sell the confidential data to a Chinese plastic production company that received government funding.
Monsanto
Another Chinese scientist has been charged with stealing trade secrets from Monsanto, a well-known agribusiness giant. In January 2022, Haitao Xiang pleaded guilty to trying to commit economic espionage. The sensitive information he was planning to sell to the Chinese government contained a software algorithm for helping farmers collect field data and increase productivity.
Working as an imaging scientist at Monsanto, Xiang managed to commit his theft by simply transferring secret data to a memory card. In April 2022, he was sentenced to more than two years in prison and fined $150,000.
General Electric Aviation
The case of Xu, who was convicted in November 2021, serves as another example of industrial espionage. This Chinese intelligence officer coordinated an operation to get access to General Electric Aviation’s unique aircraft fan technology.
Four years earlier, Xu invited a GE Aviation employee to give a presentation at the Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics. During the presentation, the host “fixed” a technical problem with a flash drive, installing malware or cloning the hard drive. When this was discovered, the GE Aviation employee managed to persuade Xu to leave China, and the intelligence officer was arrested.
Amazon
In October 2020, an undetermined number of Amazon customers received emails informing them that their email address had been “disclosed by an Amazon employee to a third party.” Amazon claims to have fired the employee in question.
There are few details on how many customers were affected, although people from all over the world reported receiving such emails. Amazon did not reveal the identity of the third party to whom the email addresses were leaked.
4 Ways to Detect and Prevent Data Misuse
Tesla
This case involves a Tesla employee who was offered $1 million by a Russian citizen for compromising data on the automotive company. Egor Kriuchkov requested an employee at Tesla’s Nevada Gigafactory to infect the company’s network with malware via email or USB drive to harvest confidential data.
Kriuchkov would then demand money from Tesla, threatening to make the data public if the company did not pay. The conspiracy was prevented before any harm was done, and Kriuchkov was arrested in August 2020.
Curiously, this wasn’t the first industrial espionage case for Tesla. Another incident occurred two years prior:
Martin Tripp, a former Tesla employee, tweeted photos of batteries he claimed to have been produced at the Gigafactory. He said they were damaged but still intended for use. An internal Tesla investigation found Tripp responsible for the leak of data besmirching Tesla to Business Insider. While Martin’s motives remain unclear, that he spied on his employer is beyond doubt.
According to an internal document leaked by Motherboard, Google dismissed about 80 employees for misusing user data and spying on customers between 2018 and 2020. Some even shared personal information with third parties. Thirty-six of these employees were fired due to security concerns in 2020.
While there is no clear evidence that Google fell victim to industrial espionage, the risk was there: 86% of security-related allegations against employees included data mishandling, such as transferring confidential data to outside parties. Whether or not these cases involve corporate espionage, similar data leaks can severely damage a company’s brand.
Volvo and Scania
Another attempt at industrial espionage happened in Sweden.
Kristian Dimitrievski was charged with providing a Russian diplomat with sensitive corporate information concerning two Swedish companies. While acting as a consultant first for Volvo Cars and then for Scania, Dimitrievski was regularly meeting with a Russian embassy official. The man was detained during one of their meetings at a restaurant in Stockholm in 2019.
As the district court stated, Dimitrievski was well aware that the information he provided would benefit Russia, thus making it a clear case of economic espionage.
7 best practices to detect and prevent industrial espionage
Anti-malware protection is just one measure in the fight against industrial espionage. You need to take more steps to strengthen the overall security posture of your organization. Follow the anti-espionage best practices we provide below and learn more on how to detect industrial espionage and prevent it.
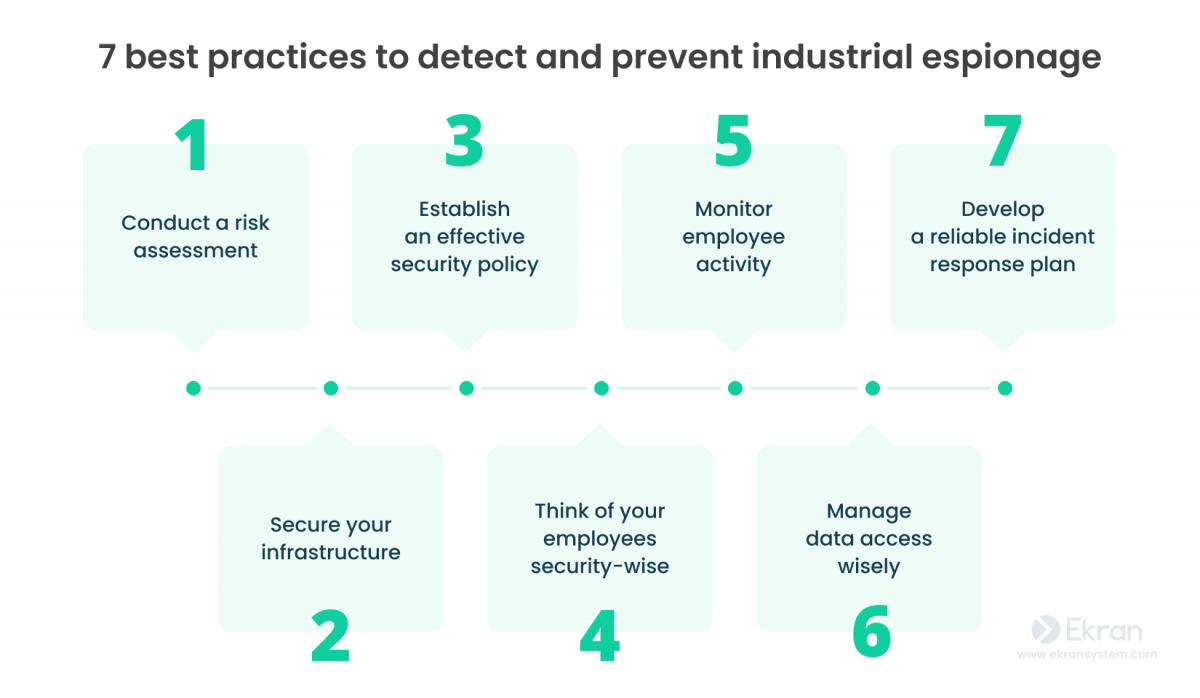


1. Conduct a risk assessment
What corporate data is the most valuable for your company?
Find potential targets. You need to know what trade secrets and other valuable data your company possesses and how desirable they are to your competitors. You can evaluate the attractiveness of your trade secrets by comparing them with products already available on the market or with known assets of your competitors.
Once you identify your most valuable data, you can guess who may want it. By knowing possible threats and potential attack vectors, you can detect vulnerabilities in your defenses.
Risk assessment is key to a risk-based security approach, which should be part of every organization’s security strategy. You should also work out a cyber incident response plan. It will help you ensure a fast and efficient response in case of a data breach to minimize its impact on your business.
2. Secure your infrastructure
Create a barrier to guard against external threats.
Establishing a secure perimeter around your company’s network is one of the pillars of cybersecurity.
Consider enhancing security at multiple levels. A layered approach provides a more complex solution against a variety of possible threats at different levels, making your security a lot harder to penetrate.
Make sure to separate your valuable data from your corporate network and limit access to it. Protect your border routers and establish screen subnets.
In addition, consider implementing a zero trust model within your corporate network. The core idea of this approach is to verify a user’s identity every time a user tries to access critical resources. The zero trust model also emphasizes the importance of limiting privileged access and validating devices. One possible tool to implement this approach is two-factor authentication.
Keep in mind that following the zero trust approach still allows for conventional corporate cybersecurity software, such as firewalls and antivirus software. Coupled with multilevel security, it will ensure an effective defense against industrial espionage via hacking and malware.
10 Must-Have Information Security Policies for Every Organization
3. Establish an effective security policy
Mitigate possible insider threats.
Establish a set of rules that will minimize the risks of industrial espionage, and formalize these rules in a clearly written cybersecurity policy.
Build the rules based on the risks you’ve identified.
While composing your cybersecurity policy, consider including rules covering the following topics:
- Network security – Include guidelines for computer network access, describe the architecture of your network security environment, and explain how security rules are implemented within it.
- Security awareness – Describe measures aimed at informing your personnel about your security procedures and mechanisms.
- Employee onboarding/termination – Define procedures for proper employee onboarding and termination in terms of security.
- Password management – Establish strict rules on how passwords must be created, stored, and managed in your organization.
- Access management – Specify procedures for providing access to various categories of data and systems for regular, privileged, and remote users.
- Audit and accountability – Describe how your system activity is monitored, analyzed, and investigated.
- Incident response – Develop a plan for what your personnel will do if a cybersecurity incident is detected.
Make sure all your employees and third parties know and follow the security rules you have developed.
A piece of advice:
Take a look at the NIST security guidelines. Depending on the type of organization you are, these guidelines will help you meet security requirements such as those found in NIST 800-53, FISMA, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. Complying with these standards and laws is crucial if you wish to run a business in a specific market or industry, such as the financial industry.
4. Think of your employees security-wise
The people you work with are crucial for sustaining a healthy and secure environment in your company. Whether it’s intentional or not, it’s frequently someone from an organization’s staff who’s responsible for industrial espionage.
As a responsible employer, assure your own faith in your personnel and eliminate all human-related risks.
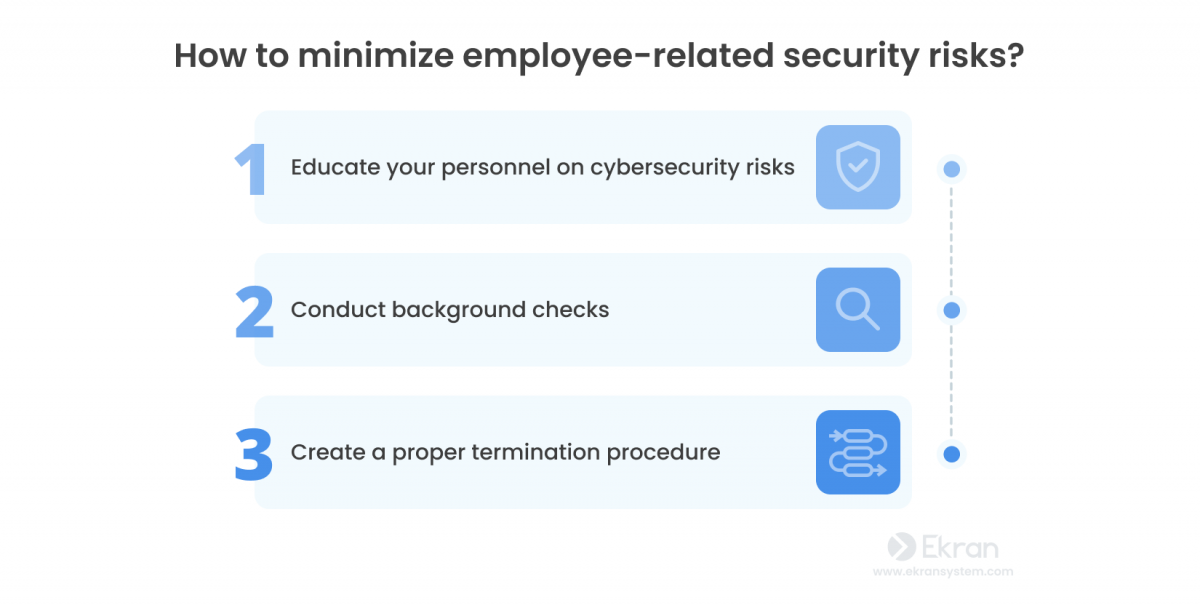


Educate employees on cybersecurity risks
Your people can become your strongest line of defense.
Make sure your employees know what insider threats are and what dangers they pose. Constantly perform cybersecurity awareness training and tell your employees about the potential consequences of insider threats for your organization. Make employees aware of the role they play in the organization’s cybersecurity and the ways they can help you improve it.
Particularly, organize regular training sessions and teach your employees about simple security practices they can use in their daily workflow. You can start with practices that will keep them safe from social engineering and help your business avoid data leaks.



Conduct employee background checks
Do you even know who works for you?
Before hiring someone, the HR department usually conducts a background check.
This minimizes the risk of getting a spy in your organization.
It can be helpful to repeat these checks once in a while – especially for employees with privileged access – to ensure they don’t become spies. A sudden surge in standards of living, unexpected trips, or paying off debt are among potential causes for concern.
Create a proper termination procedure
Are you sure your ex-employees can’t access your company’s data?
In many cases, industrial espionage is performed in the last couple weeks of an employee’s work, or even after termination. This often happens because the credentials of a terminated employee remain active, enabling them to freely access the organization’s sensitive data without anyone noticing.
You need to create and implement a proper employee termination procedure to protect your company from potential acts of industrial espionage by former workers.
Reducing the Risk of Insider Threats among New Employees
5. Monitor employee activity
What are your employees doing during their work time?
Monitoring user activity is the most common and effective measure for preventing corporate espionage. You’ll never know whether your employees act maliciously on purpose or inadvertently unless you monitor their work activity.
It’s especially important to keep an eye on privileged users, such as system administrators and upper management. They can easily gather intelligence while performing their normal tasks and explain any abnormal behavior as a mistake.
Employee monitoring makes all employee actions fully visible, allowing you to identify the attack which relates to corporate espionage and respond to it in a timely manner. In case a cybersecurity incident happens, you can use the records for your investigation.
Ekran System is a universal insider risk management platform specifically designed to combat insider threats, including industrial espionage.
By deploying Ekran System, you can monitor every action of every user of a protected endpoint, regardless of their level of access privileges. This will allow you to control the actions of system administrators and all users with access to trade secrets and financial information.
Ekran System provides you with the following user activity monitoring capabilities:
- Screen video recording. Watch user sessions in a convenient YouTube-like player and filter them by username and IP. Videos are indexed with layers of text metadata, including visited URLs, typed keystrokes, and names of opened apps.
- Search by key episodes. Advanced session analysis allows investigators to search episodes by various parameters.
- USB device monitoring and management. Monitor and control connections of all USB devices, including storage devices and other USB equipment such as modems and keyboards. Automatically allow or block USB devices according to customizable rules, blacklists, and whitelists.
Ekran System can help you comply with a wide range of government-endorsed IT standards that will benefit your company’s security.
6. Manage data access wisely
Who has access to critical data? Do they really need it?
Many companies provide all their employees with access to critical data and infrastructure by default. But while it may be convenient, this approach is not secure.
You can begin with choosing a suitable access control model for your organization. For example, you can choose between mandatory access control (MAC) and discretionary access control (DAC). Learn about the advantages and disadvantages of MAC and DAC before deciding which model works best for your organization.
Consider implementing the principle of least privilege and prohibiting access to all data unless necessary. This principle entails giving users only privileges that are essential to perform their work. Provide access to important information only to employees who really need it.
If non-privileged users occasionally need to work with confidential information, you can provide them one-time access or limit their time of work with critical resources.
By limiting the number of people with access to critical data, you significantly reduce the risks of your competitors obtaining this data. Additionally, proper access management is one of the third-party risk management best practices.
The PAM functionality in Ekran System can help you implement the above principles with ease, enabling you to:
- Granularly manage access rights of privileged and regular users
- Limit the time for which access is granted
- Automate and secure password management
Privileged Access Management: Essential and Advanced Practices
7. Develop a reliable incident response plan
What should you do when a security incident happens?
Design a plan for what your employees will do in case your company detects an incident. An incident response plan (IRP) describes who should do what when responding to a detected incident. Strict procedures will help minimize damage caused by a spy.
Ekran System brings the incident response experience to the next level. Our platform can help you proactively detect threats at the very moment they happen.
With an automated incident response system, you will be able to detect an incident and respond to it in real time:
- User and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) is an artificial intelligence-powered module that analyzes typical user activity, helping you detect unusual behavior in a timely manner.
- An actionable alert system identifies a suspicious event and notifies your security team so they can react immediately. You can choose from a collection of alert templates, or set your custom alert rules based on any suspicious event (opened URL, process name, connected USB device, etc.).
- Automated incident response acts immediately by blocking a user or showing them a warning message, terminating a suspicious process, or blocking an unapproved USB device.
On top of that:
With Ekran System, you can export all monitoring data related to a particular incident in an independent, standalone, immutable format for further investigation and analysis.
PECB Inc. Deploys Ekran System to Manage Insider Threats [PDF]
Conclusion
Whether performed by a malicious insider or a skilled hacker, industrial espionage can severely damage a company’s reputation and hinder opportunities for growth. Motivated by greed or the desire to win in a competitive race, opposing companies – and even governments – illegally use spying as their tool of choice.
To protect your business, follow the best practices discussed in this article. Start with assessing your risks, then develop and follow a robust cybersecurity policy. Combined with effective employee management and a reliable infrastructure defense, an efficient insider risk management platform like Ekran System can give you a helping hand in reducing the chance of industrial espionage happening in your organization.
Request a free trial of Ekran System and see how it works for yourself!





