Privileged users are an essential part of any organization. However, with access to commercial secrets and to the most vulnerable parts of the corporate network, they can pose high risks to your corporate cybersecurity. For this reason, the more privileges users have, the closer they need to be monitored.
Furthermore, privileged user monitoring (PUM) is a requirement of multiple laws, regulations, and data security standards including NIST 800-53, GDPR, and HIPAA. So, proper attention to privileged user monitoring and audit is a must-do for many organizations now. In this post, we describe the top 10 PUM best practices for improving the protection of your critical assets and mitigating cybersecurity risks.
Reasons for monitoring privileged users
Every organization has two main groups of users: privileged users and regular users. The access rights and permissions of privileged user accounts exceed those of other users.


While the activity of both regular and privileged users needs to be monitored, the reasons for watching each group differ. Regular users, i.e. most staff, are usually monitored to:
- Analyze employee performance
- Improve employee productivity
- Protect enterprise data and critical systems
- Mitigate insider and outsider threats
- Meet compliance requirements
On the other hand, as privileged users have access to sensitive data and systems, they’re often monitored to:
- Check who can access what
- See what changes are made in the system
- Protect enterprise data and critical systems
- Mitigate insider and outsider threats
- Meet compliance requirements
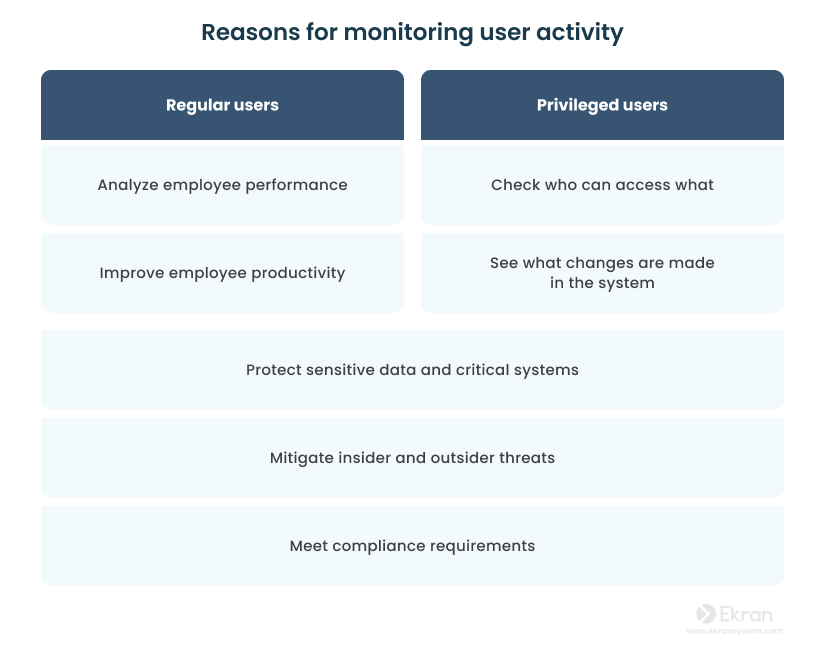

Whereas regular users are often monitored to evaluate their performance, privileged users are watched closely to make sure they don’t misuse their privileges.
Now, you may ask, “How to monitor privileged accounts effectively?”. Let’s consider the following top 10 best practices for privileged activity monitoring.
The top 10 best practices for privileged user monitoring
Even one small action can make a difference.
Today’s privileged user monitoring solutions and approaches are quite flexible, allowing you to focus on what matters most. But there’s always room for improvement. We’ve prepared a list of the top 10 best practices for PUM that can help make your cybersecurity procedures more effective and productive.


1. Fully monitor privileged user activity
Forget about partial privileged access monitoring.
User activity monitoring is resource-intensive. You need to collect large amounts of data, transfer it from monitored endpoints to a server or cloud, and store it. And the more users you need to watch over, the more resources you use. For this reason, many organizations choose partial monitoring to keep an eye only on specific types of data, systems, events, and activities.
However, halfway measures are a poor choice when it comes to privileged account activity management. As privileged users may have permanent and near-unlimited access to the most important parts of your corporate network, consider taking privileged user activity auditing seriously and watch every action of the users with elevated access.
When given a choice, go for a solution that records data in light formats, including screenshots or video recordings. The ability to search such records will also be a big plus.
Top 5 Inadvertent Mistakes of Privileged Users and How to Prevent Them
2. Limit privileges
Say “no” to unlimited privileges.
Maintaining a sufficient level of privileged user monitoring can be rather challenging. The fewer privileged users are in your organization and the fewer privileges they possess, the easier it is to monitor them appropriately.
Cyber attackers often target privileged users, as these types of accounts hold the keys to valuable information. And with unlimited privileges, malicious insiders might change system logs to conceal their crimes. Therefore, consider giving limited privileges only to a narrow circle of employees and only for a limited period of time, while keeping a close eye on each of them.
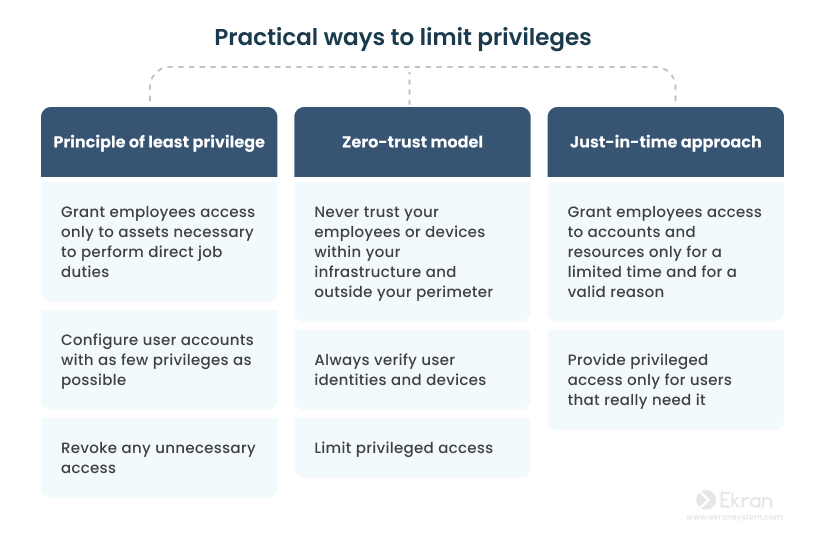

There are several approaches you can implement to limit user privileges: the principle of least privilege, a zero trust architecture, just-in-time PAM, and others.
Why Do You Need a Just-in-Time PAM Approach?
3. Obtain full visibility of all admin accounts
Get rid of shadow admins.
Privileged users can often assign the same (or lower) privileges to other users. However, assigning privileges in this way is not always properly monitored and managed. Accounts that have the same access permissions as admins but aren’t included in monitored admin groups (e.g. domain admins) are usually called shadow admins.
Poorly monitored and managed accounts with admin access rights pose a significant threat. 2023 Insider Threat Report by Gurucul reveals that 54% of insiders had credentialed access to the network and services. That’s why privileged account monitoring is of utmost importance. You should achieve full visibility over all privileged accounts to ensure the highest level of cybersecurity within your organization.
It’s crucial not only to pay attention to the activity of privileged accounts but also to their creation and deletion. Look for solutions that can analyze all network accounts and discover those with admin-level permissions. Once you’ve found all privileged accounts, perform reviews to delete unused accounts and avoid privilege creep. It’s an effective practice to make the user access review checklist and regularly follow all the steps to make sure you don’t miss a thing. Also, we reccomend you to configure all privileged accounts in a way that makes delegating user privileges or creating new shadow admins impossible.
How to Protect an Enterprise Database from Privilege Abuse
4. Closely monitor the USB devices connected to your network
Track the use of USB devices by privileged users.
A malicious insider may use a USB drive as a tool for leaking and compromising sensitive data, stealing your company’s intellectual property, or carrying out a pre-programmed attack strategy. Privileged users can cause even greater harm if they misuse USB devices and bypass security controls. To ensure the utmost protection of your organization’s data files, it is vital to monitor all the USB devices plugged into your network, especially those used by privileged users.
You may want to consider deploying USB device monitoring tools to allow you to get alerts each time a suspicious USB device is plugged in, approve or prohibit certain types of USB devices, and continuously monitor all USB device connections.
How Can Ekran System Protect You against Infected USB Devices?
5. Use secondary authentication for shared accounts
Pay very close attention to shared privileged accounts.
Some companies use shared privileged accounts to simplify their administration workflow, thereby inadvertently introducing cybersecurity risks into their IT infrastructures.
Despite being convenient, shared accounts hinder the process of user activity monitoring and auditing. It’s hard to differentiate the actions of one user from another without using specific tools.
Leveraging secondary user authentication as an additional security measure can help you clearly distinguish the activity of all shared account users while monitoring and auditing their activity.
8 Poor Privileged Account Management Practices and How to Improve Them
6. Monitor remote connections
Watch for unapproved remote logins.
Upwork reported that 37% of the U.S. labor market worked entirely remotely and 21% of employees used a hybrid work model in 2022. The more remote workers in your company, the more related security concerns may arise.
Organizations provide different groups of users with remote access to their data: regular employees, part-time workers, and subcontractors. And if these users have access to any kind of sensitive information in your network, consider implementing a remote desktop monitoring software to keep them closely monitored.
For privileged users, you should also monitor and record remote desktop protocol (RDP) sessions in the same way as local sessions. Additionally, you may consider setting strict rules, specifying which systems and data remote logins are permitted and creating whitelists of IP or MAC addresses.
Remote Employee Monitoring: How to Make Remote Work Effective and Secure
7. Make logs and records immutable
Prevent logs and records from being modified.
Depending on their permissions level, privileged users might be able to alter or delete various logs and records. At the network level, this concern can be addressed by providing unrestricted access to system logs only to a specific role or to a strictly limited group of users.
When choosing user activity monitoring software, it’s important to pick one in which modifying logs or reports is prevented by default. Having such software, you can be sure that records haven’t been tampered with.
Insider Data Theft: Definition, Common Scenarios, and Prevention Tips
8. Detect anomalies
Watch for unusual behavior.
The behavior of a legitimate user differs significantly from the behavior of an outside attacker or malicious insider. That’s why it may be challenging to detect such behavior.
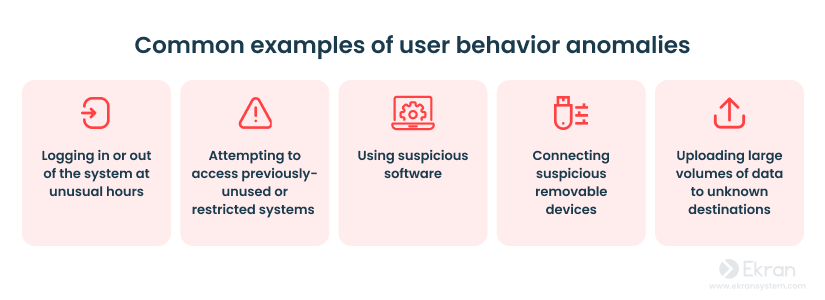

User and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) is a technology used for detecting abnormal behavior of network users. It builds a baseline behavior profile for every user or entity in the system. Based on these profiles, an UEBA system analyzes user activity and distinguishes normal actions from potentially unsafe ones.
Consider implementing UEBA technology to catch any unusual activities of your privileged users.
5 Levels of User Behavior Monitoring
9. Increase employee cybersecurity awareness
Conduct regular cybersecurity training.
Organizing security awareness training is critical for effective privileged user monitoring. Users without proper cybersecurity knowledge may not understand the necessity to monitor them and can even try to trick or sabotage the security tools and policies implemented.
Raising employees’ cybersecurity awareness can reduce the number of mistakes made by privileged users, make them more mindful of the privileges given to them, and increase their willingness to adhere to the cybersecurity procedures established in your company.
Also, when aware of how to identify cybersecurity threats, your employees are more likely to notice suspicious activity and alert you to it.
Insider Threat Awareness: What Is It, Why Does It Matter, and How Can You Improve It?
10. Perform continuous monitoring
Never take a break.
Privileged user monitoring should never be treated as a one-time event. When carried out only periodically, user activity monitoring cannot ensure full visibility of a user’s actions or properly protect critical data.
PUM is a continuous process, and should constantly be improved. Make sure you revise your privileged user monitoring and management procedures and constantly enhance them with PUM best practices and cutting-edge technology solutions. Additionally, an agile approach to access management brings flexibility and responsiveness to your organization’s cybersecurity.
Privileged Access Management vs Privileged User Management: What’s the Difference?
Monitor privileged users with Ekran System
Ekran System is a universal insider risk management platform that allows monitoring of all types of users and managing access to critical systems, applications, and data.
Ekran System can help you implement the best PUM practices, providing you with a rich set of insider threat management features:
- Continuous monitoring of all servers (including jump servers), endpoints, and remote workstations
- Managing privileged access for employees, third-party vendors, and contractors
- Context-rich user session recording of local, terminal, SSH, and RDP sessions in a searchable video format
- Gathering useful metadata on user activity such as names of run applications, visited URLs, and typed keystrokes
- Managing privileged access for employees, third-party vendors, and contractors
- Alerting and responding to cybersecurity incidents by blocking suspicious users and terminating processes
- Monitoring and management of connected USB devices, including flash drives and USB modems
- Creating detailed reports and exporting user session data for forensic investigations
All these features are essential for keeping an eye on your privileged accounts and the assets that they have access to. That’s why numerous companies choose Ekran System as a reliable all-in-one solution for monitoring privileged access.
In addition, Ekran System’s functionality can help your organization comply with SOX, HIPAA, PCI, and other cybersecurity requirements for privileged user monitoring.
Privileged User Monitoring and Auditing for a US-Based Financial Services Company [PDF]
Conclusion
Implementing best practices for privileged user monitoring is essential in today’s digital age, where insider threats and data breaches are becoming increasingly common. By effectively monitoring privileged users, organizations can prevent security threats and protect sensitive data from getting into the wrong hands.
The top 10 best practices outlined above provide a comprehensive framework for organizations to establish and maintain robust privileged user management. Employee monitoring software like Ekran System can become a cornerstone of this program. Ekran System is a trustworthy insider threat management platform that can assist you in monitoring privileged accounts, users, and third-party vendors in your organization.






